
Bipolar Disorder: The Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Manic and Depressive States
Mania and depression are two distinct states often observed in bipolar disorder, each with its unique characteristics and impact on an individual’s behavior, thoughts, and overall functioning. Here’s a detailed analytical description of both:
Mania
Mania is a state of abnormally elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and energy levels. It’s more than just feeling extremely happy or upbeat; it’s a profound alteration in mood and behavior that goes beyond normal bounds and can severely impact daily functioning.
Characteristics:
– Elevated Mood: This can manifest as excessive happiness, euphoria, or extreme irritability.
– Increased Energy and Activity Levels: A marked rise in goal-directed activity or physical restlessness.
– Rapid Thought and Speech Patterns: Jumping quickly from one idea to another (flight of ideas) or experiencing ‘pressured speech’ where talking fast feels compulsory.
– Decreased Need for Sleep: Feeling rested after only a few hours of sleep.
– Grandiosity: Inflated self-esteem or grandiose beliefs about one’s abilities.
– Impaired Judgment: Engaging in risky behaviors without considering the consequences, like reckless driving or impulsive financial decisions.
– Distractibility: Easily pulled off task or unable to focus.
– Psychosis (in severe cases): Losing touch with reality, experiencing delusions or hallucinations.
Impact:
– Manic episodes can severely disrupt life, straining relationships, work performance, and leading to dangerous situations. Despite the initial ‘high,’ the aftermath often includes significant personal and professional consequences.
Depression
Depression, on the other hand, is characterized by a pervasive low mood, loss of interest or pleasure in almost all activities, and a range of other cognitive and physical symptoms.
Characteristics:
– Persistent Sadness or Emptiness: An overwhelming feeling of gloom or despair.
– Anhedonia: Loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed.
– Fatigue or Loss of Energy: Feeling tired almost all the time.
– Feelings of Worthlessness or Guilt: Disproportionately blaming oneself for various faults or failures.
– Changes in Appetite and Sleep Patterns: Significant weight loss or gain, insomnia, or hypersomnia.
– Difficulty Concentrating: Struggling to focus, remember, or make decisions.
– Psychomotor Agitation or Retardation: Noticeable restlessness or slowing down of physical movements.
– Recurrent Thoughts of Death or Suicide: Persistent thoughts about death, suicidal ideation, or suicide attempts.
Impact:
– Depression can be debilitating, affecting every aspect of life. It can lead to social withdrawal, deteriorating performance at work or school, and serious health complications.

In bipolar disorder, an individual may cycle between these two states, experiencing the extreme highs of mania and the crushing lows of depression. Each phase brings its challenges and risks, necessitating a comprehensive treatment approach that often includes medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding the distinct nature of mania and depression is crucial in managing bipolar disorder effectively and helping those affected lead stable, fulfilling lives.
Bipolar disorder, a complex psychiatric condition, is characterized by dramatic mood swings between manic and depressive states. These mood swings are not just emotional responses but are deeply rooted in the brain’s chemistry. Understanding the impact of daily habits, such as caffeine consumption in the morning and alcohol intake at night, on these mood swings is crucial in managing bipolar disorder.
The Role of Caffeine and Alcohol
 Caffeine, a known stimulant, can potentially trigger a manic state in individuals with bipolar disorder. Consuming caffeine in the morning might provide a burst of energy and elevated mood, simulating a manic phase.
Caffeine, a known stimulant, can potentially trigger a manic state in individuals with bipolar disorder. Consuming caffeine in the morning might provide a burst of energy and elevated mood, simulating a manic phase.
 Conversely, alcohol, a depressant, consumed in the evening, can lead to feelings of sadness or lethargy, mirroring a depressive state. While these substances don’t cause bipolar disorder, they can exacerbate its symptoms, making mood swings more pronounced and challenging to manage.
Conversely, alcohol, a depressant, consumed in the evening, can lead to feelings of sadness or lethargy, mirroring a depressive state. While these substances don’t cause bipolar disorder, they can exacerbate its symptoms, making mood swings more pronounced and challenging to manage.
Gambling and Bipolar Disorder
 Gambling behavior provides an interesting lens to view bipolar disorder. The thrill of winning can mimic the euphoria of a manic episode, while the despair of losing can plunge an individual into a depressive state. This similarity raises questions about the nature of bipolar disorder – is it just an extreme version of the highs and lows everyone experiences? The key difference lies in the intensity and impact of these mood swings on an individual’s life, often requiring medical intervention.
Gambling behavior provides an interesting lens to view bipolar disorder. The thrill of winning can mimic the euphoria of a manic episode, while the despair of losing can plunge an individual into a depressive state. This similarity raises questions about the nature of bipolar disorder – is it just an extreme version of the highs and lows everyone experiences? The key difference lies in the intensity and impact of these mood swings on an individual’s life, often requiring medical intervention.
Other Behaviors and Emotional Responses
People with bipolar disorder may exhibit other behaviors that align with their mood states. During manic phases, they might engage in risky or impulsive activities, while depressive states can lead to withdrawal and disinterest in previously enjoyable activities. It’s important to understand that these behaviors are symptoms of the disorder, not personal choices.
Treatment and Management
The treatment of bipolar disorder often involves medication to stabilize mood swings. However, lifestyle modifications, such as regulating caffeine and alcohol intake, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and engaging in stress-reducing activities, can be equally important. Recognizing and adjusting these behaviors can provide significant relief and contribute to overall stability.
Bipolar disorder is a complex condition that affects individuals in various ways. While lifestyle choices like caffeine and alcohol consumption or gambling behaviors can influence mood states, they are not the sole cause of the disorder. Effective management includes a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments. By understanding and respecting the impact of our daily choices on our mental health, we can take proactive steps towards stability and wellness.
 Here’s a list of other behaviors that can create extreme differences in mood, particularly for individuals with mood disorders such as bipolar disorder:
Here’s a list of other behaviors that can create extreme differences in mood, particularly for individuals with mood disorders such as bipolar disorder:
- Substance Use: Beyond caffeine and alcohol, the use of drugs like cocaine, amphetamines, or even certain prescription medications can induce mood swings.
- Sleep Patterns: Drastic changes in sleep patterns, such as staying up all night or sleeping excessively, can lead to significant mood shifts.
- Physical Activity: Both the lack of exercise and extreme over-exertion can affect mood. Regular moderate exercise tends to stabilize mood, while its absence or extremes can cause fluctuations.
- Dietary Habits: Consumption of high-sugar, high-fat, or heavily processed foods can affect mood. Conversely, sudden dieting or fasting can also have mood-altering effects.
- Social Interactions: Intense social activities or social isolation can lead to mood swings. For some, overwhelming social engagements can induce stress or euphoria, while loneliness can contribute to depressive states.
- Stressful Events: Exposure to high-stress situations, whether positive (like a job promotion) or negative (such as loss of a loved one), can trigger extreme mood changes.
- Seasonal Changes: Some individuals experience mood shifts with changes in seasons, a condition known as Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
- Overworking: Engaging in long hours of work without adequate breaks can lead to stress and subsequent mood swings.
- Screen Time: Excessive use of screens, especially before bedtime, can disrupt sleep and mood patterns.
- Shopping or Spending Sprees: For some, compulsive shopping can lead to a temporary high, followed by guilt or depression, especially in the context of financial strain.
It’s important to note that while these behaviors can affect mood, they do not necessarily cause mood disorders. However, for individuals with conditions like bipolar disorder, these behaviors can exacerbate symptoms or trigger mood episodes. As always, moderation and balance are key, and professional guidance is recommended for managing mood disorders.
 Bipolar disorder is typically managed with a combination of medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. The most commonly prescribed medications for bipolar disorder fall into several categories, each working in different ways to help stabilize mood and reduce the severity of symptoms:
Bipolar disorder is typically managed with a combination of medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. The most commonly prescribed medications for bipolar disorder fall into several categories, each working in different ways to help stabilize mood and reduce the severity of symptoms:
- Mood Stabilizers – Lithium: One of the oldest and most widely used mood stabilizers. It helps to reduce the severity and frequency of mania and can also help alleviate depressive episodes. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it’s believed to affect the flow of sodium through nerve and muscle cells in the body, influencing the excitation or mania.
– Anticonvulsants: Medications like valproate (Depakote), lamotrigine (Lamictal), and carbamazepine (Tegretol) are also used as mood stabilizers. Originally developed to treat seizures, these drugs can help stabilize mood swings in bipolar disorder. They are thought to work by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain, thereby stabilizing mood.
- Antipsychotics – Atypical antipsychotics, such as olanzapine (Zyprexa), risperidone (Risperdal), quetiapine (Seroquel), aripiprazole (Abilify), and lurasidone (Latuda) are often used, especially when symptoms of mania or mixed episodes are prominent. These medications can help control symptoms like delusions or hallucinations. They work by affecting various neurotransmitters in the brain, including dopamine and serotonin.
- Antidepressants – While antidepressants are sometimes used to treat bipolar depression, they must be used cautiously as they can sometimes trigger a manic episode. They are often prescribed in combination with a mood stabilizer or antipsychotic. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft) are common choices.
- Antidepressant-Antipsychotic – The combination drug fluoxetine-olanzapine (Symbyax) combines the antidepressant fluoxetine and the antipsychotic olanzapine. It works by targeting both serotonin and dopamine neurotransmitters in the brain, and is used to treat depressive episodes associated with bipolar I disorder.
- Calcium Channel Blockers – Though less commonly used, some calcium channel blockers like verapamil, typically used to treat high blood pressure, may have mood-stabilizing effects.
- Benzodiazepines – Short-term use of benzodiazepines can help with sleep or anxiety. However, they are generally not used long-term due to the risk of addiction.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness and side effects of these medications can vary greatly from person to person. Treatment is often highly individualized, requiring careful monitoring and adjustments by a healthcare professional. Additionally, the exact mechanisms of how some of these medications work in bipolar disorder are not entirely understood and are the subject of ongoing research.
 Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely used therapy technique for a variety of mental health conditions, including bipolar disorder. It focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors to improve mood and functioning. Some effective CBT strategies for bipolar disorder include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely used therapy technique for a variety of mental health conditions, including bipolar disorder. It focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors to improve mood and functioning. Some effective CBT strategies for bipolar disorder include:
- Mood Monitoring: Keeping a daily record of moods, sleep patterns, and life events, which can help in identifying triggers and patterns associated with mood swings.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Learning to recognize and change distorted or negative thought patterns that can contribute to emotional and behavioral problems.
- Stress Management: Developing coping strategies to manage stress, which can often trigger or exacerbate bipolar episodes.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Enhancing the ability to effectively solve problems that arise, which can reduce the stress and helplessness that sometimes accompany bipolar disorder.
- Lifestyle Management: Assisting individuals in establishing a healthy routine, including regular sleep patterns and balanced activities, which can help stabilize mood swings.
- Interpersonal Skills: Focusing on improving relationships, which can be strained by the symptoms of bipolar disorder, and developing better communication and conflict-resolution skills.
- Relapse Prevention: Identifying early signs of mood episodes and developing strategies to manage them effectively.
These techniques are typically used in conjunction with medication and other treatments under the guidance of a mental health professional. If you or someone you know is struggling with bipolar disorder, it’s important to seek professional help.
Learn More
Help for Pornography and Sex Addiction: A Guide to Self-Help and Professional Support through Applied Behavioral Sciences
Acknowledging and seeking help for pornography and sex addiction is a crucial step toward recovery. This article explores a dual approach—self-help strategies and professional assistance—highlighting the resources available through Applied Behavioral Sciences (ABS) at ABSbehavioralHealth.com
Self-Help Strategies:
- Educate Yourself:
– Gain insights into the nature of addiction and its impact on mental health through reputable sources, books, and online materials.
– Explore resources that provide guidance on overcoming pornography and sex addiction.
- Self-Reflection:
– Engage in honest self-reflection to identify triggers and underlying emotional issues contributing to the addiction.
– Maintain a journal to track thoughts and feelings associated with addictive behaviors.
- Establish Healthy Habits:
– Cultivate positive habits, including regular exercise, mindfulness, and sufficient sleep, to support overall well-being.
– Create a structured daily routine to minimize idle time that may lead to relapse.
Professional Help through Applied Behavioral Sciences:
- Visit ABSBEHAVIORALHEALTH.COM:
– Navigate to the official website of Applied Behavioral Sciences (ABS) to explore the array of services offered for addiction treatment.
– Gain insights into the ABS approach to behavioral health and addiction recovery.
- Contact Applied Behavioral Sciences:
– Utilize the contact information provided on the website to reach out for assistance.
– Engage with the responsive and knowledgeable staff at Applied Behavioral Sciences to discuss personalized treatment options.
- Comprehensive Assessment:
– Applied Behavioral Sciences conducts thorough assessments to understand the unique aspects of each individual’s addiction.
– Professionals at ABS work with clients to develop tailored treatment plans.
- Evidence-Based Therapies:
– ABS employs evidence-based therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), to address the root causes of addiction.
– Specialized therapists guide clients through the recovery process with empathy and expertise.
- Group and Individual Counseling:
– Benefit from both group and individual counseling sessions to address personal challenges and connect with others going through similar experiences.
– Applied Behavioral Sciences fosters a supportive community environment.
- Family Involvement:
– Recognizing the impact of addiction on families, ABS encourages family involvement in the recovery process.
– Family therapy sessions can strengthen communication and understanding.
- Aftercare and Support:
– Applied Behavioral Sciences provides aftercare and ongoing support to prevent relapse and promote sustained recovery.
– Alumni programs and community resources contribute to a continuum of care.
Overcoming pornography and sex addiction involves a combination of self-help strategies and professional support. Applied Behavioral Sciences (ABS) offers a comprehensive and compassionate approach to addiction recovery, addressing the unique needs of each individual. By taking the first step toward seeking help, individuals can embark on a journey of healing, growth, and lasting change. Visit ABSbehavioralHealth.com to explore the resources available and initiate your path to recovery.
Learn More
10 Symptoms of Sex Addiction: When Desire Becomes a Compulsion
Sexuality is a natural and healthy aspect of human life. However, for some individuals, the pursuit of sexual pleasure can escalate into a problematic and compulsive behavior known as sex addiction. While not officially recognized as a mental disorder, sex addiction can profoundly impact a person’s life and well-being. In this blog, we will delve into the ten common symptoms of sex addiction, shedding light on the signs that may indicate the need for professional help, such as therapy offered at ABS Applied Behavioral Sciences.
-
Preoccupation with Sexual Thoughts
One of the earliest signs of sex addiction is an incessant preoccupation with sexual thoughts. Individuals may find themselves constantly fantasizing about sexual encounters, even when it interferes with their daily responsibilities and activities.
-
Escalating Sexual Activities
Over time, individuals with sex addiction may engage in increasingly risky or extreme sexual behaviors to achieve the same level of satisfaction. This escalation can include experimenting with dangerous or taboo practices.
-
Compulsive Pornography Consumption
Sex addiction often involves a compulsive consumption of pornography. Individuals may spend hours each day viewing explicit material, leading to negative consequences in their personal and professional lives.
-
Frequent Masturbation
Excessive masturbation is another symptom of sex addiction. Individuals may engage in this behavior compulsively, sometimes to the detriment of their physical and emotional well-being.
-
Multiple Extramarital Affairs
Individuals with sex addiction may find themselves in multiple extramarital affairs, seeking novelty and variety in sexual partners to fulfill their desires. This can lead to severe strain on existing relationships.
-
Inability to Control Sexual Behaviors
A hallmark of addiction is the inability to control one’s behavior despite negative consequences. Individuals with sex addiction often engage in sexual activities even when they know it could lead to personal, professional, or legal problems.
-
Neglecting Responsibilities
As sex addiction takes hold, individuals may neglect their responsibilities at work, home, or in other areas of life. This can result in job loss, strained relationships, and financial difficulties.
-
Secretive Behavior
Sex addicts often engage in secretive behaviors to hide their activities from loved ones. This can include maintaining hidden stashes of pornography, lying about their whereabouts, or engaging in anonymous sexual encounters.
-
Mood Swings and Emotional Distress
Sex addiction is often accompanied by mood swings and emotional distress. Individuals may experience guilt, shame, anxiety, and depression as a result of their compulsive sexual behaviors.
-
Failed Attempts to Quit
Despite recognizing the negative consequences of their actions, individuals with sex addiction may repeatedly attempt to quit or control their behaviors without success. This pattern of failure can be frustrating and disheartening.

Seeking Professional Help at ABS Applied Behavioral Sciences
If you or someone you know is struggling with impulsive sexual behavior and exhibits the symptoms of sex addiction, it is crucial to seek professional help. At ABS Applied Behavioral Sciences, our team of experts specializes in providing therapy and support for individuals facing sex addiction and related issues.
Therapy can play a pivotal role in helping individuals with sex addiction understand the underlying causes of their compulsive behaviors, develop healthy coping mechanisms, and work towards a more balanced and fulfilling life. Our experienced therapists are dedicated to guiding individuals through the recovery process, offering a safe and non-judgmental space for healing.
Conclusion
Sex addiction can have a profound impact on an individual’s life, leading to physical, emotional, and social complications. Recognizing the ten common symptoms of sex addiction is the first step towards seeking help and embarking on a journey of recovery. If you or someone you know is struggling with sex addiction, don’t hesitate to reach out to professionals like those at ABS Applied Behavioral Sciences. With the right support and therapy, individuals can regain control over their lives and find a path to healthier, more satisfying relationships and behaviors.
Learn More
Behind the Wheel – The Unseen Fight Against DUI
We can make a difference with a simple act of courage or care, saving a life from danger.
The statistics are sobering – every 45 minutes, someone in the United States dies in a drunk driving-related crash. Behind these numbers lies immense grief and suffering. How to prevent the senseless loss of life and help every person arrive home safely?
The Struggle is Real
DUI incidents inflict profound personal, communal, and societal wounds. Survivors are often left with severe emotional trauma, disability, or lost loved ones. Yet many suffer silently, too ashamed or pained to speak out. This isolates victims when community support is most needed during the healing process. Meanwhile, drunk driving crashes cost the U.S. over $50 billion annually from medical expenses, legal costs, lost productivity, and property damage.
Despite increased public awareness, drunk driving still accounts for nearly one-third of all traffic fatalities nationwide.
Consequences of DUI
Beyond the obvious risk of causing grave physical harm or death, DUI convictions carry severe legal and personal consequences spanning years – all entirely avoidable with proper planning. Legally, offenders face:
- License suspension
- Ignition interlock device installation
- Fines up to $10,000
- Jail time
- Those who injure or kill someone while intoxicated face catastrophic emotional trauma and lengthy imprisonment for vehicular manslaughter.
DUI charges also:
- Limit future job prospects
- Restrict personal freedoms
- Lead to social stigma
- The impacts resonate for years, choosing to drive impaired ones that should never be taken lightly.
Challenges and Potential Solutions
While resources exist for rehabilitation, eliminating drunk driving remains an unfinished agenda. Counseling and therapy can be prohibitively expensive and waitlists for free/low-cost programs are often extremely long. Additionally, the social stigma surrounding addiction issues creates barriers – offenders may feel too ashamed or hopeless to acknowledge their struggles.
Many also lack awareness of the available options, continuing risky behaviors like drunk driving. Expanding access through funding help programs, delivering public education destigmatizing treatment, and promoting services could encourage more people to pursue help. Removing obstacles around rehabilitation can put redemption within reach for many.
Seeking Help, Saving Lives
Driving under the influence is frequently a manifestation of underlying personal challenges related to addiction, which necessitate professional assistance. Several resources exist to help offenders achieve behavioral change through rehabilitation programs and counseling. These services connect people facing substance abuse challenges and provide tools to work through issues collectively. Local community health centers may offer affordable therapy options as well.
Conclusion
Seeking help benefits more than just the individual – it saves lives lost needlessly through drunk driving when addiction problems persist untreated. By acknowledging alcoholism and getting support, offenders gain tools to establish new patterns, becoming part of the ‘Vision Zero’ solution. There is always hope for change if one has the courage and willingness to redeem themselves. Getting assistance can help break the dangerous cycle of addiction and drunk driving.
Learn More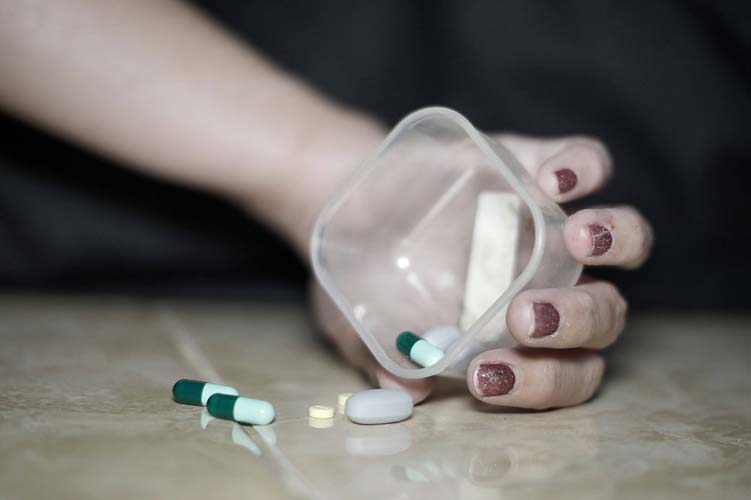
Behind Closed Doors – Confronting the Inner Struggles of Addiction
Caught in its grip, shame and isolation breed an unbearable loneliness, incomprehensible to outsiders.
Addiction casts a wide net in today’s society. Its grasp touches people from all walks of life – the wealthy, the impoverished, the young, the old. Behind closed doors, a silent battle wages within those facing the demons of addiction. In public view, many put on a mask of normalcy to hide their inner turmoil. The stigma surrounding addiction drives many to suffer alone rather than seek support.
The Hidden Reality Behind the Mask
Addiction cleverly hides behind a facade of normalcy. To the outside world, those in the clutches of addiction often appear perfectly fine. They go to work, care for their families, and manage their daily responsibilities. Few would guess the internal chaos and profound struggle hidden under their public mask. Societal norms and expectations make it difficult to address addiction openly. No one wants to be viewed as flawed or somehow less than. So the mask stays in place, hiding the truth of their pain.
Escaping the Stigma
Surrounding addiction drives many to endure their struggles in secrecy and solitude rather than seek support. Judgmental attitudes cultivate an environment of fear that prevents openness. Specifically, individuals with addiction often fear:
- Ridicule or loss of social status from peers
- Professional repercussions such as loss of a job or damaged career prospects
- Inflicting shame upon their families and friends
- Being viewed as flawed, unstable, or somehow defective
- Receiving blame for their condition rather than treatment or help
The threat of condemnation and disgrace carries more perceived risk than the anguish of addiction itself. As a self-preservation reaction, it becomes easier to deny, conceal, rationalize, or minimize an addiction than to risk social and professional fallout from admitting they have a problem.
The Loneliness Within
- Addiction Supplants Human ConnectionAddiction cultivates acute loneliness. As Substance abuse and addiction strengthen their foothold, they often supplant relationships with people. The chemical or behavior becomes their primary coping mechanism, their closest confidant. Human intimacy and vulnerability carry more perceived risk than the reliability of their addiction. With no one to confide in, each day becomes consumed with hiding the truth and pretending everything is fine. This lonely facade eventually takes an extreme mental and emotional toll.
- Shame Perpetuates IsolationDeep shame and guilt also generate reluctance to open up about their struggles. They feel too flawed, too broken to burden others with the horror they perceive within themselves. Every failed attempt at sobriety heightens their sense of shame. This spiraling cycle strengthens the chokehold of isolation and destructive behaviors characteristic of addiction.
The Battle Against Shame
To break addiction’s grasp, we must first disarm the shame that fuels it. Those struggling must reframe addiction as an illness requiring treatment, not a personal failure requiring punishment. They must extend empathy, compassion, and self-forgiveness to themselves as a necessary first step in healing. By recognizing that their brokenness is not defined by their intrinsic worth, space is created to move beyond shame into self-love and acceptance. This new foundation enables building the coping strategies and networks of support vital to overcoming addiction’s ravages.
Seeking Help Behind Closed Doors
Healing begins when conversations come out from behind closed doors. We all have a role to play in fostering safe spaces for people to open up about addiction or mental health struggles. As friends and family members, we can communicate our unconditional support. As colleagues, we can encourage policies that foster openness around addiction and facilitate financial access to assistance programs. As a society, we must advocate for increasing and improving mental health and addiction resources. Healing happens through human connection. By linking arms with compassion as allies against addiction’s isolation, we can help shatter the masks behind which addiction thrives.
Conclusion
The pain of addiction is profound, and it can’t heal in secrecy. Let compassion and understanding replace the stigma and silence that used to exist. To all those fighting unseen battles with addiction’s cruelty, may you find the courage to reach out beyond loneliness – and discover you don’t have to walk this road alone. Support and hope await all seeking help, no matter how broken and unworthy you may feel.
Learn More
Understanding the Severity and Complications of Sex Addiction
Sex addiction, also known as hypersexual disorder or compulsive sexual behavior disorder, is a complex and controversial issue that has garnered significant attention in recent years. It refers to a condition in which individuals engage in repetitive and intense sexual behaviors despite facing negative consequences. This article explores the severity and complications related to sex addiction, shedding light on the physical, psychological, and social implications of this condition.
1. Defining Sex Addiction
Sex addiction is not officially recognized as a mental disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the authoritative guide for mental health professionals. However, it is acknowledged by many experts as a behavioral addiction that can profoundly impact a person’s life. Individuals with sex addiction often struggle with an overpowering urge to engage in sexual activities, which may include pornography consumption, anonymous sex, compulsive masturbation, or multiple extramarital affairs. The lack of an official diagnosis has led to debates about its classification and treatment.
2. Severity and Complications
A. Physical Complications
- Risk of Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Individuals with sex addiction may engage in high-risk sexual behaviors, such as unprotected intercourse or sex with multiple partners, which increases their vulnerability to STIs, including HIV/AIDS.
- Physical Injuries: The pursuit of extreme sexual activities can lead to physical harm, such as injuries related to bondage, sadomasochistic practices, or excessive sexual activity.
- Exhaustion and Fatigue: Excessive sexual behaviors can result in physical exhaustion and fatigue, negatively affecting an individual’s overall health and well-being.

B. Psychological Complications
- Depression and Anxiety: Sex addiction is often accompanied by feelings of guilt, shame, and anxiety. These emotions can exacerbate mental health issues and contribute to a cycle of compulsive behavior.
- Low Self-Esteem: The secrecy and shame associated with sex addiction can lead to a significant decline in self-esteem and self-worth.
- Relationship Issues: Sex addiction can take a toll on relationships, leading to trust issues, jealousy, and infidelity. Partners of individuals with sex addiction often experience emotional trauma.
- Escalation of Desires: Over time, individuals with sex addiction may require more extreme or taboo sexual experiences to achieve the same level of satisfaction, leading to a dangerous escalation of desires.

C. Social Complications
- Isolation: Sex addiction can lead to social isolation as individuals become consumed by their compulsive behaviors and may withdraw from friends and family.
- Legal Consequences: Engaging in illegal or socially unacceptable sexual activities, such as voyeurism or public indecency, can lead to legal trouble and criminal charges.
- Financial Issues: The pursuit of sexual satisfaction may result in financial strain due to excessive spending on pornography, escort services, or other sexual activities.
III. Treatment and Recovery
Recognizing the severity and complications associated with sex addiction is crucial for individuals seeking help. Treatment options include:
- Psychotherapy: Individual and group therapy sessions can help individuals explore the root causes of their addiction, develop coping strategies, and address underlying emotional issues.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to address underlying mental health conditions such as depression or anxiety.
- Support Groups: Participating in sex addiction support groups can provide a sense of community and encouragement for recovery.
- Couples Therapy: Couples affected by sex addiction may benefit from therapy to rebuild trust and address the impact of the addiction on the relationship.
Sex addiction is a complex and challenging condition that can have severe physical, psychological, and social complications. While it remains a subject of debate and controversy, it is essential to recognize the suffering experienced by individuals affected by sex addiction and to offer them appropriate support and treatment options. By understanding the severity and complications of sex addiction, we can work towards a more compassionate and effective approach to addressing this complex issue.
Compulsive sexual behavior, often referred to as sex addiction, is a challenging and distressing condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s life and relationships. Those struggling with compulsive sexual behavior may find it difficult to control their impulses, leading to harmful consequences in their personal, social, and professional lives. Fortunately, professional psychotherapy offers a ray of hope for individuals seeking help to overcome this condition. This article will explore how cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and group therapy, offered at places like Applied Behavioral Sciences Outpatient Therapy and statewide through online telemedicine, can be instrumental in the recovery journey of those with compulsive sexual behavior.

Understanding Compulsive Sexual Behavior
Compulsive sexual behavior is characterized by an obsessive preoccupation with sexual thoughts, fantasies, or behaviors, often to the detriment of one’s well-being and daily functioning. Individuals with this condition may engage in excessive pornography consumption, frequent casual sexual encounters, or other risky sexual behaviors. These patterns of behavior can lead to feelings of guilt, shame, and anxiety, creating a cycle that is difficult to break without professional help.
The Role of Psychotherapy in Recovery
Professional psychotherapy is a vital component in the treatment of compulsive sexual behavior. Therapists trained in addressing this condition can help individuals gain insight into the underlying causes of their behavior and develop strategies to manage and overcome their compulsions. Two effective therapeutic approaches commonly used in the treatment of compulsive sexual behavior are cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and group therapy.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a widely recognized and evidence-based therapeutic approach that has proven effective in treating compulsive sexual behavior. This therapy helps individuals identify and challenge distorted thoughts and beliefs related to their sexual behaviors. By working with a trained therapist, clients can develop healthier thought patterns and learn new coping skills to reduce their compulsive behaviors.
CBT for compulsive sexual behavior typically includes the following components:
- Identifying triggers: Clients learn to recognize the situations, emotions, or thoughts that trigger their compulsive sexual behavior.
- Developing coping strategies: Therapists help clients develop healthier coping mechanisms to manage their triggers and reduce the urge to engage in compulsive behavior.
- Building relapse prevention plans: Clients work on strategies to prevent relapse and maintain their progress over time.
- Addressing underlying issues: Therapists assist clients in exploring and addressing any underlying emotional, psychological, or relational issues that may contribute to their compulsive behavior.
- Group Therapy

Group therapy offers a unique and supportive environment for individuals with compulsive sexual behavior to share their experiences, challenges, and successes with others who can relate. Led by trained therapists, group therapy sessions provide a sense of community and connection that can be highly therapeutic.
Key benefits of group therapy for compulsive sexual behavior include:
- Reduction of isolation: Individuals often feel isolated and ashamed due to their compulsive behaviors. Group therapy provides a safe space for them to connect with others who understand their struggles.
- Accountability: Group members can hold each other accountable for their progress, providing motivation and support.
- Learning from others: Group therapy allows participants to learn from the experiences and strategies of their peers, offering new perspectives and insights.
- Building healthier relationships: Group therapy can help individuals improve their interpersonal skills and develop healthier relationships.
Accessing Therapy at Applied Behavioral Sciences Outpatient Therapy and Online Telemedicine
Applied Behavioral Sciences Outpatient Therapy and other reputable treatment centers offer specialized programs for individuals dealing with compulsive sexual behavior. These programs often incorporate a combination of individual therapy, group therapy, and additional support services to address the unique needs of each client.
In addition to traditional in-person therapy, many treatment centers now offer online telemedicine services, making it easier for individuals to access professional help from the comfort and privacy of their own homes. Telemedicine has proven to be an effective and convenient way to receive therapy, especially for those who may face barriers such as geographic distance or scheduling conflicts.

Compulsive sexual behavior is a challenging condition, but it is treatable with the right professional support. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and group therapy, offered at places like Applied Behavioral Sciences Outpatient Therapy and through online telemedicine, have shown promising results in helping individuals regain control over their lives and build healthier relationships. Seeking professional help is the first step on the path to recovery, and with the right guidance, individuals with compulsive sexual behavior can find healing and hope for a brighter future.
Learn More

10 Effective Ways to Motivate Someone to Quit Marijuana
Quitting marijuana can be a challenging journey for many, but with the right motivation and support, it’s entirely possible. If you’re looking to encourage someone to break free from marijuana, here are ten detailed strategies that can help pave the way to a healthier lifestyle.
1. Understand the ‘Why’
Get to the root of why they want to quit. Is it for health reasons, financial savings, or improved relationships? Help them to visualize the benefits of quitting by discussing and documenting the positive changes they can expect.
2. Set Clear Goals
Encourage setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Whether it’s cutting back gradually or quitting cold turkey, having clear milestones can be incredibly motivating.
3. Create a Supportive Environment
A supportive environment can make all the difference. Be the cheerleader and the coach. Offer to join them in activities that distract from cravings, like exercising, watching movies, or exploring new hobbies.
4. Replace the Habit
Help them find healthier habits to replace marijuana use. This could be anything from meditation and yoga to painting or writing. New hobbies can provide a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment.
5. Manage Triggers
Together, identify triggers that prompt marijuana use and develop strategies to manage them. This might include avoiding certain social situations or finding new ways to deal with stress and anxiety.
6. Celebrate Milestones
No victory is too small to celebrate. Acknowledge every milestone, whether it’s the first day without marijuana or the first month. Celebrations reinforce positive behavior and provide encouragement to keep going.
7. Offer Compassion and Understanding
Be a source of compassion and understanding. Quitting can be an emotional rollercoaster, and knowing someone is there to listen without judgment can be incredibly reassuring.
8. Educate on the Effects
Sometimes, individuals aren’t aware of the long-term effects of marijuana use. Provide them with resources or suggest informative documentaries that highlight how quitting can lead to a healthier mind and body.
9. Encourage a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy body fosters a healthy mind. Motivate them to eat well, exercise regularly, and maintain a regular sleep schedule to support their overall well-being and reduce the urge to smoke.
10. Professional Support
Finally, remind them that it’s okay to seek professional help. Whether it’s a counselor, a support group, or a treatment program, professional assistance can offer tailored advice and strategies.

Seeking Professional Help
Embarking on the journey to quit marijuana is a personal decision and one that can be filled with challenges. However, it’s important to remember that professional help is readily available and can provide the necessary guidance and support.
At ABS (Applied Behavioral Sciences), individuals can find a range of services from counseling to personalized treatment plans. ABS’s team of dedicated professionals is committed to helping each person find their path to recovery. Don’t hesitate to reach out and take that first step towards a healthier, marijuana-free life.
For more information on the services provided by ABS, please visit their website or contact their helpline. Remember, asking for help is a sign of strength, and with the right support, anyone can overcome their dependence on marijuana.
Learn More